Bee or Yellow Jacket Sting
Is this your child's symptom?
- Sting from a bee, hornet, wasp, or yellow jacket
- Over 95 percent of stings are from honey bees or yellow jackets
- The main symptoms are pain and redness
Cause of Bee Sting Reactions
- The bee's stinger injects venom into the skin.
- The venom is what causes the symptoms.
Local Skin Reactions to the Sting
- The main symptoms are pain, itching, swelling and redness at the sting site.
- Pain. Severe pain or burning at the site lasts 1 to 2 hours. Itching often follows the pain.
- Swelling. The bee sting may swell for 48 hours after the sting. The swelling can be small or large. Stings on the face can cause a lot of swelling around the eye. It looks bad, but this is not serious. The swelling may last for 7 days.
- Redness. Bee stings are often red. That doesn't mean they are infected. Infections rarely happen with stings. The redness can last 3 days.
Anaphylactic Reaction to the Sting
- A severe life-threatening allergic reaction is called anaphylaxis.
- The main symptoms are hives with trouble breathing and swallowing. It starts within 2 hours of the sting.
- This severe reaction to bee stings happens in 4 out of a 1,000 children.
- Hives. After a bee sting, some children just develop hives all over or face swelling. Hives or face swelling alone may be able to be treated at home. But, at times, these symptoms can also lead to anaphylaxis. Be sure to call your doctor now to help decide.
Prevention of Bee Stings
- Don't go barefoot if bees are around.
- Be careful in gardens and orchards.
- Insect repellents do not work against these stinging insects.
See More Appropriate Topic (instead of this one):
- If NOT, try one of these: Insect Bite
When to Call Us for Bee or Yellow Jacket Sting
Call 911 Now
- Past severe allergic reaction to bee stings (not just hives) and stung less than 2 hours ago
- Wheezing or trouble breathing
- Hoarseness, cough or tightness in the throat or chest
- Trouble swallowing or drooling
- Speech is slurred
- Acts or talks confused
- Passed out (fainted) or too weak to stand
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- More than 5 stings for 10 pounds (5 kg) of weight. In teens, more than 50 stings.
- Fever and sting looks infected (spreading redness)
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- More than 72 hours since the sting and redness getting larger. Note: infection is not common. Redness that starts in the first 24 hours is due to venom.
- Swelling is huge (4 inches or 10 cm). It spreads across a joint such as the wrist.
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Normal reaction to bee, wasp, or yellow jacket sting
Care Advice for Bee or Yellow Jacket Sting
What You Should Know About Bee Stings:
- Bee stings are common.
- The main symptoms are pain and redness.
- The swelling can be large. This does not mean it's an allergy.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
Try to Remove the Stinger (if present):
- Only honey bees leave a stinger.
- The stinger looks like a tiny black dot in the sting.
- Use a fingernail or credit card edge to scrape it off.
- If the stinger is below the skin surface, leave it alone. ?It will come out with normal skin shedding.
Meat Tenderizer for Pain Relief:
- Make a meat tenderizer paste with a little water. Use a cotton ball to rub it on the sting. Do this once for 20 minutes. Reason: this may neutralize the venom and reduce the pain and swelling. Caution: do not use near the eye.
- If you don't have any, use an aluminum-based deodorant. You can also put a baking soda paste on the sting. Do this for 20 minutes.
Cold Pack for Pain:
- If pain does not improve after using the meat tenderizer paste, rub with an ice cube.
- Do this for 20 minutes.
Pain Medicine:
- To help with the pain, give an acetaminophen product (such as Tylenol).
- Another choice is an ibuprofen product (such as Advil).
- Use as needed.
Steroid Cream for Itching:
- For itching or swelling, put 1% hydrocortisone cream (such as Cortaid) on the sting.
- No prescription is needed.
- Use 3 times per day.
Allergy Medicine for Itching:
- If itching becomes severe, give a dose of Benadryl.
- No prescription is needed. Age limit: 1 and older.
What to Expect:
- Severe pain or burning at the site lasts 1 to 2 hours.
- Normal swelling from venom can increase for 48 hours after the sting.
- The redness can last 3 days.
- The swelling can last 7 days.
Call Your Doctor If:
- Trouble breathing or swallowing occurs (mainly during the 2 hours after the sting). Call 911.
- Redness gets larger after 3 days
- Swelling becomes huge (4 inches or 10 cm)
- Sting starts to look infected
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
Remember! Contact your doctor if you or your child develop any "Contact Your Doctor" symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
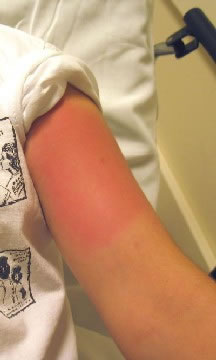
Bee Sting of Upper Arm
This photo shows a localized reaction to a bee sting. There is mild redness in an oval 4 inches (10 cm) wide of the left upper arm.
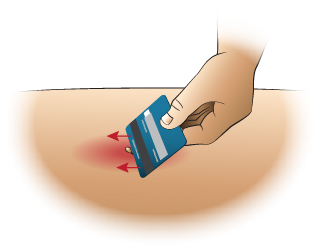
First Aid - Removing a Stinger
The stinger looks like a tiny black dot in the center of the sting. There are many different methods of removal. Removing the stinger quickly is more important than the method of removal used.
- You can scrape it out with a credit card or finger nail.
- You can also use adhesive tape.
- If only a small fragment remains, don't worry about it. It will shed with the skin.
Special Notes:
- In many cases no stinger will be present.
- Only bees leave their stingers. Wasps, yellow jackets and hornets do not.
Copyright 2000-2025 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.



